According to the CDC, more than 34 million Americans have diabetes. Of those with the condition, between 90% and 95% have Type 2.
While Type 2 typically affects adults over 45, it’s becoming more common in children and teens as well.
Here’s what you need to know to get the facts about Type 2 diabetes.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Your pancreas produces a hormone called insulin. Its job is to let the glucose in your bloodstream into your body’s cells to provide them with energy.
For those with Type 2 diabetes, the cells don’t respond to the hormone correctly. As a result, blood sugar levels increase to unsafe levels.
The longer the condition goes unmanaged, the more at risk you are for serious health complications.
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
You have a greater risk of developing Type 2 diabetes if you:
- Are overweight or obese
- Are over the age of 45
- Have a family history of Type 2 diabetes
- Are not very physically active
- Have ever had gestational diabetes or given birth to a baby weighing more than nine pounds
- Have high blood pressure, heart disease, or high triglycerides
- Are a smoker
How Is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes requires a medical exam. If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should schedule an appointment with your health care provider:
- Blurry vision
- Excessive thirst
- Increased urination
- Hunger
- Increased infections
- Wounds that don’t heal
- Feeling fatigued or worn out constantly
- Tingling or numbness in your hands or feet
In addition to going over your symptoms, your doctor will likely order one or more tests. These tests might include:
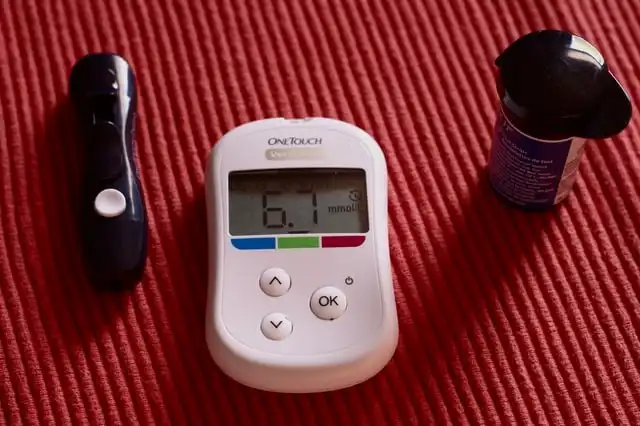
- Fasting plasma glucose test, which tests your blood sugar levels on an empty stomach
- A1c test, which shows the average of your blood glucose over two to three months
- Oral glucose tolerance test, which checks your blood sugar levels before and two hours after drinking something sweet
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Some people with Type 2 diabetes can lower their blood sugar levels with diet and exercise alone. Lifestyle changes to help manage the condition include:
- Exercising regularly (at least 30 to 60 minutes a day)
- Eating a healthier diet (reducing calorie intake, cutting back on refined carbs and sweets, incorporating more fresh fruits and vegetables)
- Losing weight
- Monitoring your blood sugar levels
If altering your lifestyle isn’t enough to get your blood sugar levels under control, your doctor will likely prescribe medication to help.
Metformin is typically the first medication recommended. It lowers the amount of glucose your liver makes and helps your body to respond better to insulin.
Other medications for managing Type 2 diabetes include:
- Sulfonylureas or meglitinides such as glipizide or nateglinide, which help your body to produce more insulin
- Victoza, an injectable medication that slows digestion and lowers blood sugar levels
- Trulicity, a once-weekly injection that helps to improve A1c and blood sugar levels while helping your body to release its own insulin
- Long-lasting insulin shots
Make Your Medications More Affordable
If your doctor prescribes medication for your Type 2 diabetes, RxLess can help you to get your prescription for less.
Using our online search tool, you can find discounts on your specific medication at nearby pharmacies. Choose the offer best suited for you and bring it with you when you go to the pharmacy to pick up your prescription.
The offer is free, and you pay the discounted price at checkout.